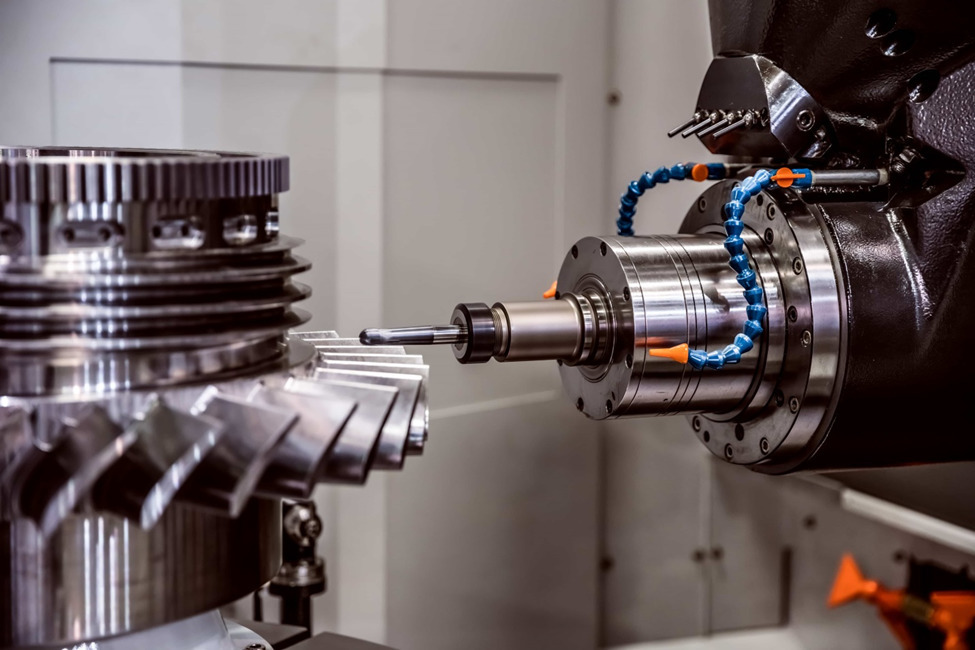
The computer numerical controlled milling process is a revolution in the machine shops and that is what gives you the ability to mass-produce these detailed components faster and with very high accuracy. The setting up of the program takes time and once it is done, more pieces can be further produced at very faster rates that have great part-to-part repeatability. Hence, this is how it became very ideal for high-volume manufacturing.
This process is having the accuracy mapped by the computer controls and that entirely checks the rotation and position of the multi-point cutting tools. A tool moves along with the three primary axes, namely X, Y, Z for precision cutting. This happens through proceeding through the pre-programmed machining operations. The geometries complicate when the axes increase to 5 to cater to more detailed and intricate designs.
Here, let us now understand what the milling methods can be:
- Plain milling- This is the other name for surface milling. Here a cutting tool is used to remove the materials along the surface area of the workpieces.
- Face milling- Rotational axis perpendicular upon the material surface. The grinding and the cutting tools face down against the workpiece surface to create the desired shape.
- Angular milling- This method has its rotational axis positioned perpendicular to the surface material. Cutting or grinding is followed next.
- Form milling- These methods create almost non-flat cuts and help create contours, curves as well as radii. The specific tools are going to create accurate form cuts.
CNC milling machines always require parts, you can check for CNC milling parts here.
But the classifications do not just end here. There are also a variety of milling machines that are used to cater to industrial requirements. They are:
- Horizontal milling- The mounted cutting tool contains a spindle that is oriented horizontally as it moves along the workpiece. This machine can handle a lot of deeper and heavier cuts through thicker as well as shorter cutting tools.
- Vertical milling- This contains the vertically-oriented spindle and moves up and down the stationary workpiece. These spindles move across perpendicular and parallel axes.
- Multi-axis milling- These involve the 4-axis and 5-axis CNC mills. They provide heavily detailed as well as complex machine operations, which take place quite easily. They work along the X, Y, and Z axes and in addition, on the A and B axes.
You can rely on the LOCUS Precision milling for industry-grade parts, created as per the requirements, however, large or small.